From Robots to Algorithms: How AI is Transforming Manufacturing
From Robots to Algorithms: How AI is Transforming Manufacturing
Explore how Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry with automation, efficiency, and innovation.

Introduction
The manufacturing industry is at the forefront of a technological revolution driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI). From robots on assembly lines to predictive algorithms in supply chain management, AI is redefining how products are designed, produced, and delivered. By automating processes, improving quality control, and enhancing productivity, AI is paving the way for a smarter, more efficient future in manufacturing.
This article explores the transformative impact of AI on manufacturing, focusing on its applications, benefits, and potential to shape the industry’s future.
1. Advanced Automation and Robotics
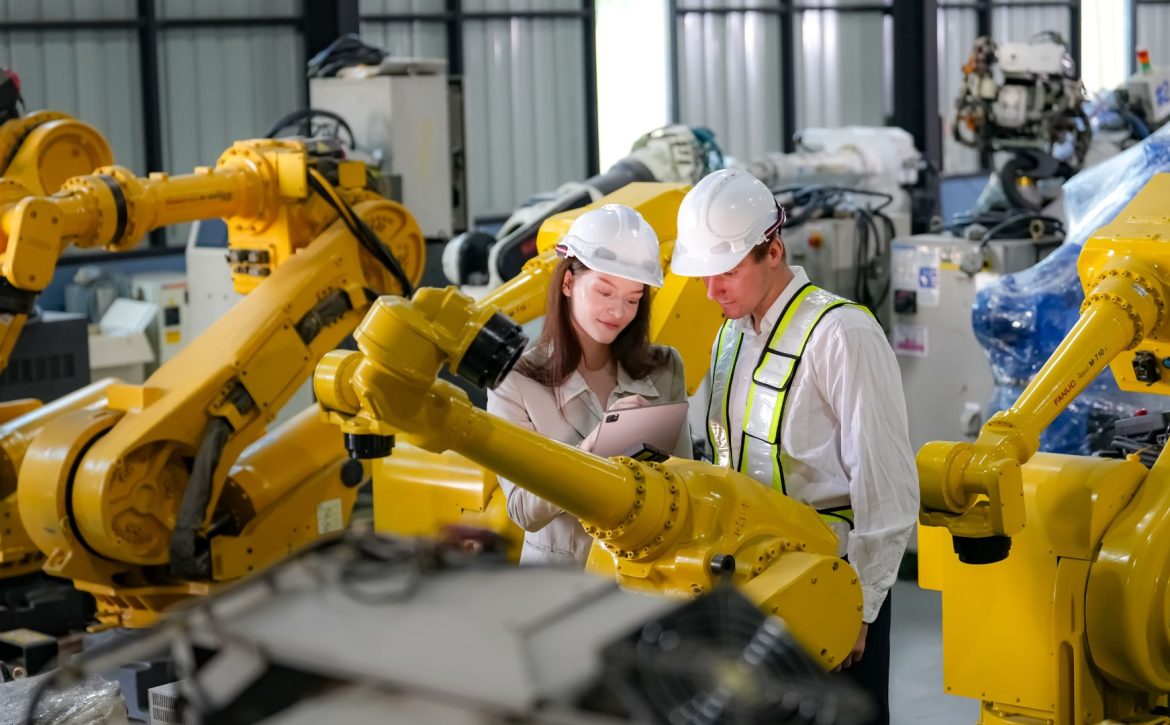
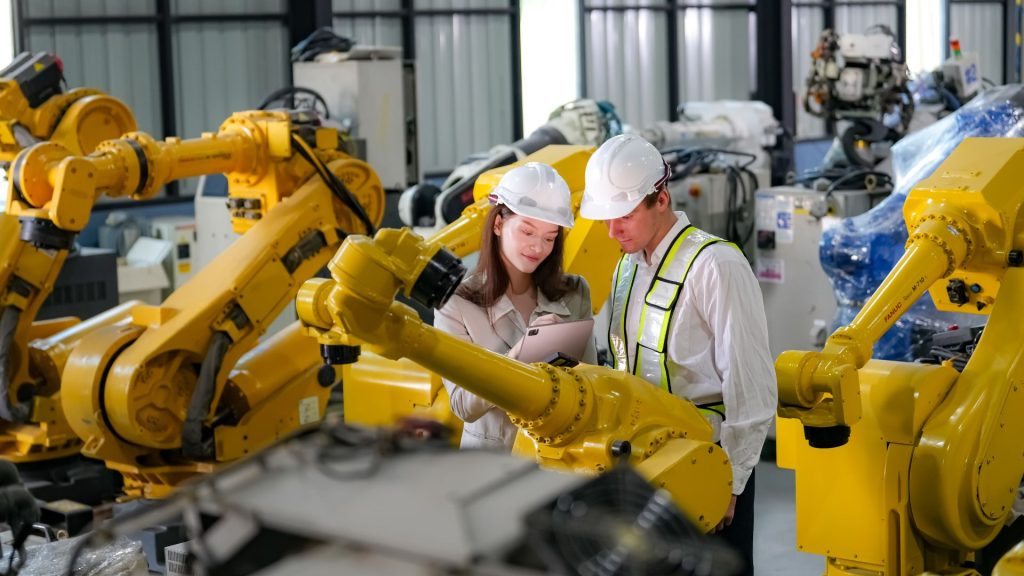
Robots powered by AI have become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. These intelligent machines perform repetitive tasks with precision and consistency, such as assembly, welding, and material handling. Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside human employees, enhancing productivity while reducing physical strain.
AI enables robots to learn and adapt to new tasks through machine learning algorithms, making them versatile and efficient in dynamic manufacturing environments.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Equipment downtime can significantly impact manufacturing efficiency and profitability. AI-powered predictive maintenance systems analyze sensor data to identify potential issues before they lead to failures. By predicting maintenance needs, manufacturers can reduce unplanned downtime, extend equipment lifespan, and lower repair costs.
For example, manufacturers use AI to monitor vibrations, temperature, and other metrics in machinery, enabling timely interventions that prevent disruptions.
3. Enhancing Quality Control
AI-driven vision systems are transforming quality control by detecting defects with unparalleled accuracy. These systems analyze images and identify irregularities in products, such as scratches, dents, or misalignments, that may be missed by the human eye. AI algorithms continuously improve through machine learning, ensuring higher standards of quality over time.
This precision minimizes waste and enhances customer satisfaction, providing a competitive edge in the market.
4. Optimizing the Supply Chain
AI plays a critical role in streamlining supply chain operations. By analyzing data on demand patterns, inventory levels, and logistics, AI algorithms optimize production schedules and delivery routes. This ensures that materials are available when needed and that products reach customers efficiently.
Companies like Siemens and GE are leveraging AI to enhance supply chain visibility, reduce costs, and improve responsiveness to market demands.
5. Accelerating Product Design and Innovation
AI is revolutionizing product design by enabling generative design processes. Engineers input design constraints into AI software, which then generates multiple iterations optimized for performance, cost, and manufacturability. This approach accelerates innovation and reduces development cycles.
AI also supports simulations and virtual testing, allowing manufacturers to refine products before physical prototypes are created, saving both time and resources.
6. Driving Sustainability
AI is helping manufacturers adopt more sustainable practices by optimizing resource usage and reducing waste. Energy management systems powered by AI monitor and adjust energy consumption across facilities, minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, AI assists in recycling processes by sorting materials more effectively and improving reuse strategies.
By integrating AI into sustainability initiatives, manufacturers can align with environmental goals while maintaining profitability.
7. The Future of AI in Manufacturing
The future of AI in manufacturing is marked by continued advancements in robotics, IoT integration, and autonomous decision-making. As AI becomes more sophisticated, manufacturers will benefit from fully connected factories where machines communicate and collaborate to optimize production.
Innovations like digital twins and quantum computing will further enhance AI’s capabilities, enabling unprecedented levels of efficiency and innovation in manufacturing.
Conclusion
From robots on the factory floor to algorithms optimizing supply chains, AI is transforming every aspect of manufacturing. These technologies improve efficiency, enhance quality, and drive innovation, enabling manufacturers to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in manufacturing will expand, paving the way for smarter, more sustainable, and resilient production processes. By embracing AI, manufacturers can unlock new opportunities and redefine the future of the industry.