Accelerating Your Business Growth with
Cutting-Edge Digital Business Solutions
LET’S TALK

Augmenting Your Business Growth with
Groundbreaking A.I.
LET’S TALK

Bringing Revolutionary Ideas to Reality with
Mobile Application
LET’S TALK

Accelerating Your Business Growth with
Cutting-Edge Digital Business Solutions
LET’S TALK

Augmenting Your Business Growth with
Groundbreaking A.I.
LET’S TALK

Bringing Revolutionary Ideas to Reality with
Mobile Application
LET’S TALK

Accelerating Your Business Growth with
Cutting-Edge Digital Business Solutions
LET’S TALK


4.5/5

5/5
100% on time | 100% customer satisfaction.
Solving Complex Problems in
Healthcare withAI

 Maximize your Medicare/Medicaid ROI With a Powerful & Affordable PlatformFor businesses who need clarity, productive communication, prioritisation and accountabilityLearn more
Maximize your Medicare/Medicaid ROI With a Powerful & Affordable PlatformFor businesses who need clarity, productive communication, prioritisation and accountabilityLearn more 
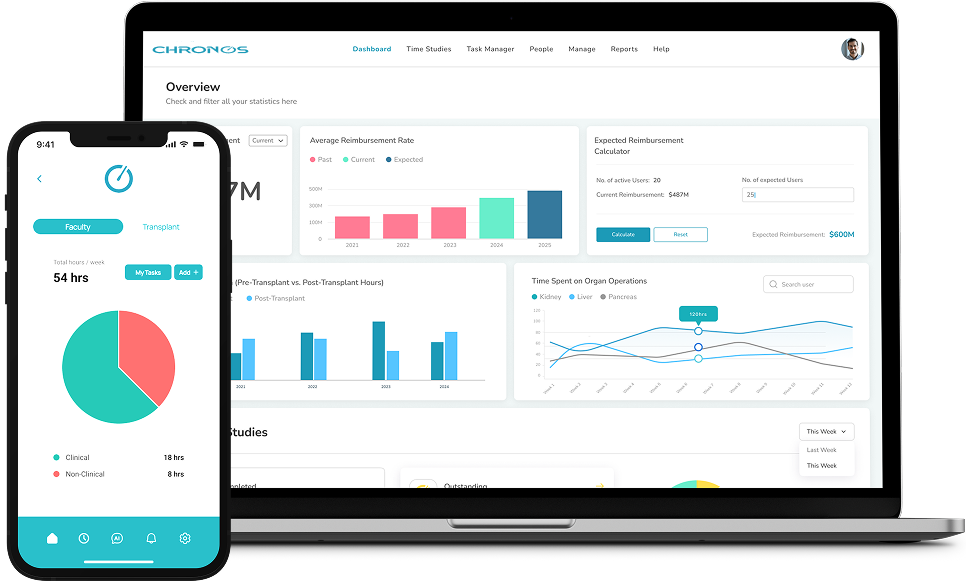
 Improving quality of Life and Increasing Life Longevity for Elderly.Provides the perfect solution for seniors living in the USA or all over the globe with little to no assistance.Learn more
Improving quality of Life and Increasing Life Longevity for Elderly.Provides the perfect solution for seniors living in the USA or all over the globe with little to no assistance.Learn more 

 Revolutionizing Healthcare Data Exchange with DOCLINQA cutting-edge healthcare platform that streamlines patient care with AI-driven appointment scheduling, intelligent risk assessment, and seamless medical data management.Learn more
Revolutionizing Healthcare Data Exchange with DOCLINQA cutting-edge healthcare platform that streamlines patient care with AI-driven appointment scheduling, intelligent risk assessment, and seamless medical data management.Learn more 

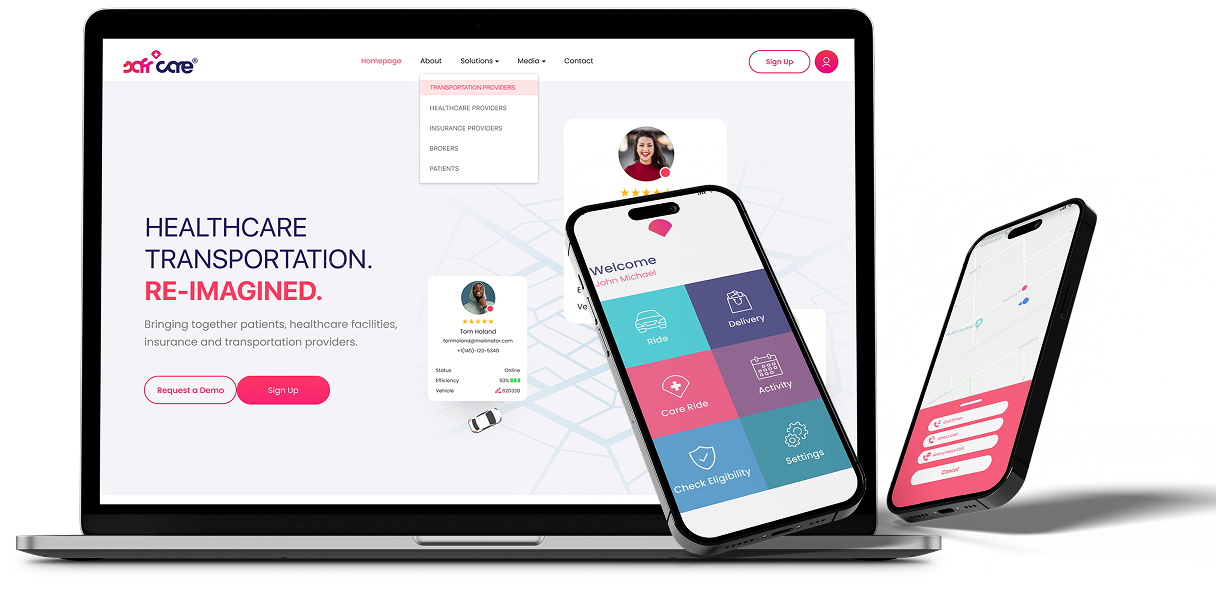
 Healthcare Transportation. Reimagined.Reimagining the medical transportation ecosystem with out-of-the box thinking.Learn more
Healthcare Transportation. Reimagined.Reimagining the medical transportation ecosystem with out-of-the box thinking.Learn more 
 Maximize your Medicare/Medicaid ROI With a Powerful & Affordable PlatformFor businesses who need clarity, productive communication, prioritisation and accountabilityLearn more
Maximize your Medicare/Medicaid ROI With a Powerful & Affordable PlatformFor businesses who need clarity, productive communication, prioritisation and accountabilityLearn more 

 Improving quality of Life and Increasing Life Longevity for Elderly.Provides the perfect solution for seniors living in the USA or all over the globe with little to no assistance.Learn more
Improving quality of Life and Increasing Life Longevity for Elderly.Provides the perfect solution for seniors living in the USA or all over the globe with little to no assistance.Learn more 

 Revolutionizing Healthcare Data Exchange with DOCLINQA cutting-edge healthcare platform that streamlines patient care with AI-driven appointment scheduling, intelligent risk assessment, and seamless medical data management.Learn more
Revolutionizing Healthcare Data Exchange with DOCLINQA cutting-edge healthcare platform that streamlines patient care with AI-driven appointment scheduling, intelligent risk assessment, and seamless medical data management.Learn more 

 Healthcare Transportation. Reimagined.Reimagining the medical transportation ecosystem with out-of-the box thinking.Learn more
Healthcare Transportation. Reimagined.Reimagining the medical transportation ecosystem with out-of-the box thinking.Learn more 

 Maximize your Medicare/Medicaid ROI With a Powerful & Affordable PlatformFor businesses who need clarity, productive communication, prioritisation and accountabilityLearn more
Maximize your Medicare/Medicaid ROI With a Powerful & Affordable PlatformFor businesses who need clarity, productive communication, prioritisation and accountabilityLearn more 

Highly Experienced Teams
100000+
SATISFIED USERS OF OUR PRODUCTS
100+
YEARS OF COMBINED EXPERIENCE
Cutting-Edge Technology
Services Under One Roof!
Services we can provide:
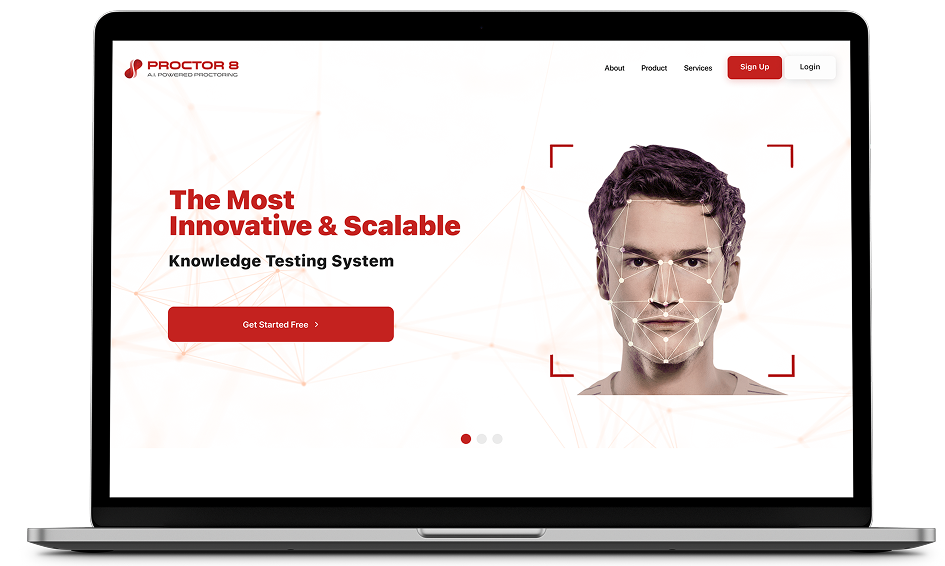
Proctor8- The Most Innovative & ScalableProctor8 is a fully cloud-based platform that provides end-to-end proctoring services.Learn more 
InteRoads - Most Advanced & Powerful Automated Testing SystemInteRoads is the industry’s most advance, intuitive, and powerful automated knowledge and road testing platform.Learn more .37810c4c.png)

KTS- Knowledge Testing Solutions KTS lets you run unlimited tests in any language across all locations — all from one simple dashboard. Sign up now for your 30-day free trial!Learn more 

Proctor8- The Most Innovative & ScalableProctor8 is a fully cloud-based platform that provides end-to-end proctoring services.Learn more 

InteRoads - Most Advanced & Powerful Automated Testing SystemInteRoads is the industry’s most advance, intuitive, and powerful automated knowledge and road testing platform.Learn more .37810c4c.png)

KTS- Knowledge Testing Solutions KTS lets you run unlimited tests in any language across all locations — all from one simple dashboard. Sign up now for your 30-day free trial!Learn more 

Proctor8- The Most Innovative & ScalableProctor8 is a fully cloud-based platform that provides end-to-end proctoring services.Learn more 

Code Snippets.
Introducing Simple Interval Reminder/Timer Chrome extension!Are you looking for an easy way to set reminders or timers while you browse the web? Look no further! Our extension is designed to help you stay organized and on track with your tasks.Learn more 

Introducing the AI Tweet Generator BotIntroducing the AI Tweet Generator Bot, your ultimate tool for crafting captivating and engaging tweets! Powered by cutting-edge artificial intelligence technology, this bot is designed to assist users in generating high-quality tweets effortlessly.Learn more 
.57c3d0b5.png)
Introducing the AI Upwork Proposal Generator Botis a powerful Chrome extension designed to assist freelancers in crafting compelling proposals on the Upwork platform. Leveraging the capabilities of artificial intelligence, this extension generates customized proposals by analyzing job descriptions and generating relevant proposal content.Learn more 

Introducing Simple Interval Reminder/Timer Chrome extension!Are you looking for an easy way to set reminders or timers while you browse the web? Look no further! Our extension is designed to help you stay organized and on track with your tasks.Learn more 

Introducing the AI Tweet Generator BotIntroducing the AI Tweet Generator Bot, your ultimate tool for crafting captivating and engaging tweets! Powered by cutting-edge artificial intelligence technology, this bot is designed to assist users in generating high-quality tweets effortlessly.Learn more 
.57c3d0b5.png)
Introducing the AI Upwork Proposal Generator Botis a powerful Chrome extension designed to assist freelancers in crafting compelling proposals on the Upwork platform. Leveraging the capabilities of artificial intelligence, this extension generates customized proposals by analyzing job descriptions and generating relevant proposal content.Learn more 

Introducing Simple Interval Reminder/Timer Chrome extension!Are you looking for an easy way to set reminders or timers while you browse the web? Look no further! Our extension is designed to help you stay organized and on track with your tasks.Learn more 

Schedule your free consultancy today.
Cutting Edge Labor
Market Solutions
The #1 Job Board for Hiring or Finding your next jobCareer.VI is the Virgin Islands' #1 Job website. This great platform allows Virgin Islands employers to post their job openings absolutely free. If you are looking for jobs in St. Croix, St. Thomas, St John, Tortola, Virgin Gorda, Anegada, Jost Van Dyke and Caribbean Jobs, Career.VI provides you one stop resource to find and apply for all USVI and BVI jobs.

Make Better Decisions with 360 InsightNinjaHR is built to meet the changing needs of HR for small to growing teams. Our cloud-based HR system grows with your needs without breaking your wallet. Elevate your HR, simplify your processes, get 360 insight and retain best talent with Ninja HR.

The #1 Job Board for Hiring or Finding your next jobCareer.VI is the Virgin Islands' #1 Job website. This great platform allows Virgin Islands employers to post their job openings absolutely free. If you are looking for jobs in St. Croix, St. Thomas, St John, Tortola, Virgin Gorda, Anegada, Jost Van Dyke and Caribbean Jobs, Career.VI provides you one stop resource to find and apply for all USVI and BVI jobs.

Make Better Decisions with 360 InsightNinjaHR is built to meet the changing needs of HR for small to growing teams. Our cloud-based HR system grows with your needs without breaking your wallet. Elevate your HR, simplify your processes, get 360 insight and retain best talent with Ninja HR.

The #1 Job Board for Hiring or Finding your next jobCareer.VI is the Virgin Islands' #1 Job website. This great platform allows Virgin Islands employers to post their job openings absolutely free. If you are looking for jobs in St. Croix, St. Thomas, St John, Tortola, Virgin Gorda, Anegada, Jost Van Dyke and Caribbean Jobs, Career.VI provides you one stop resource to find and apply for all USVI and BVI jobs.



Contact Us.
Talk to us and
get your project moving!
We will respond to you within 24 hours.
You’ll be talking to product and tech experts (no account managers).


Areas We Serve
Lahore
Hally Tower
Pakistan
Boston
100 Powdermill road, Suit 127, Acton MA 01720
USA
Lahore
Hally Tower
Pakistan
Boston
100 Powdermill road, Suit 127, Acton MA 01720
USA
Lahore
Hally Tower
Pakistan


